Control systems are crucial in various industries, influencing automation and efficiency. According to a recent report by the International Society of Automation, 75% of companies acknowledge the importance of managing these systems effectively.
Dr. Emily Carter, an expert in control systems, emphasizes, "Understanding these systems is key to optimizing performance." This insight highlights that many organizations struggle to leverage their control systems fully. Effective management often requires both technical skills and strategic thinking.
Implementing control systems can yield significant benefits, yet many companies face challenges. Data from Control Engineering reveals that nearly 30% of firms consider their control systems underutilized. This gap indicates a need for reflection and improvement. Organizations should prioritize education, collaboration, and continuous improvement in this area.

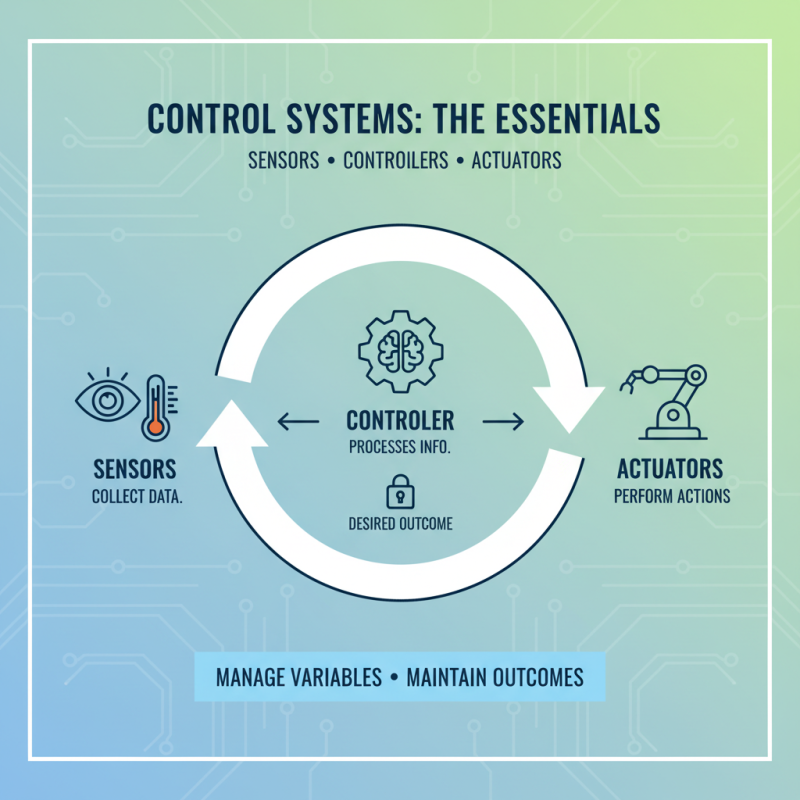
Control systems are essential in many fields, from engineering to everyday life. They help manage variables to maintain desired outcomes. Understanding basic concepts is key. A control system comprises sensors, controllers, and actuators. Sensors collect data, while controllers process this information. Actuators perform actions based on controller commands.
It's essential to grasp the functionality of feedback in control systems. Feedback loops can be positive or negative. Positive feedback amplifies changes, while negative feedback stabilizes systems. Each type serves its purpose, but misuse can lead to instability. For instance, too much positive feedback may cause systems to overshoot their targets.
Common issues arise from misconceptions in control systems. Many mistakenly think systems run perfectly. In reality, they often have flaws. Delays in sensors can hinder response times. Additionally, environmental factors frequently affect performance. Awareness of these limitations fosters improvement. By evaluating control systems critically, one can ensure better management and understanding.
Feedback mechanisms are crucial in control systems. They enable continuous monitoring and adjustments based on output performance. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, effective feedback controls can improve system efficiency by up to 30%. This highlights the significance of real-time data analysis in stimulating system responses.
Implementing feedback correctly isn’t always straightforward. It requires understanding how inputs influence outputs. Too much reliance on past performance can lead to errors. Research shows that 40% of businesses experience feedback lag, meaning their systems react too slowly. This delay can render controls ineffective.
Tip: Regularly review your system's feedback loops. Ensure they are responsive and timely. Small adjustments can lead to significant improvements. Embrace imperfections in initial implementations; they can provide valuable insights for refinement.
Analyzing control system stability is crucial in engineering and automation. Stability determines how a system responds to disturbances. An unstable system can lead to poor performance and even failure. Understanding the key metrics that influence stability is essential.
One common method for assessing stability is through root locus analysis. This technique helps visualize how system poles move with changes in gain. A system with poles in the left half of the complex plane is stable. However, if they shift right, problems arise. Be mindful of these dynamics.
Tip: Always simulate various scenarios before implementation. This can reveal potential issues in stability that may not be obvious at first glance.
Another approach is frequency response analysis. By examining how a system reacts to different frequencies, engineers can identify critical points. Gain and phase margins provide insight into how close a system is to instability. If margins are too low, be cautious.
Tip: Regularly review stability margins. They can change with system modifications, possibly leading to challenges.
Remember, perfect stability is often an illusion. Real-world systems are complex. Always be ready to adapt your strategies, as stability is not guaranteed. Reflect on system behavior, and use metrics to guide your management.
Managing control systems effectively requires the right tools. Software solutions play a crucial role. They help monitor, analyze, and optimize system performance. User-friendly interfaces make it easier for operators. Dashboards can display real-time data, showing trends and alerts.
Many tools offer automation features. These can reduce manual errors and save time. However, not every tool fits every situation. Choosing the wrong software can lead to mismanagement. In some cases, overly complex systems may confuse operators. Simplicity often trumps complexity. Reflecting on user feedback can help improve system effectiveness.
It's important to track software updates and training. Often, teams overlook these steps, resulting in poor usage. Regular training sessions can empower staff. They build confidence and ensure everyone is on the same page. Decision-makers should continually assess software effectiveness. This allows for timely adjustments and improvements in control system management.
| Tool/Software | Description | Key Features | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|---|
| MATLAB | A high-level language and interactive environment for numerical computation, visualization, and programming. | Control system toolbox, simulation, and optimization tools. | Engineers, researchers in academia and industry. |
| Simulink | A block diagram environment for modeling, simulating and analyzing dynamic systems. | Model-based design, built-in blocks for control system modeling. | System engineers, control engineers. |
| LabVIEW | A system-design platform and development environment for a visual programming language. | Graphical programming, real-time data acquisition, various analysis tools. | Researchers, control engineers in modal and data acquisition. |
| SCADA Systems | Supervisory control and data acquisition systems for industrial control. | Real-time monitoring, control, and data logging capabilities. | Manufacturing, water and waste management, energy sectors. |
| PID Controllers | Control loop feedback mechanisms widely used in industrial control systems. | Proportional, Integral, and Derivative control capabilities. | Automation industries, robotics. |
Effective control systems are crucial for any organization aiming for continuous improvement. According to a recent report by the International Society of Automation, organizations that implement robust control strategies can see productivity enhancements of up to 30%. But managing these systems is often a challenge. It's not just about technology; it's about the integration of people, processes, and data.
Continuous improvement should be a shared responsibility. Teams must engage in regular feedback loops to refine their control processes. A survey indicated that 62% of employees felt they were not adequately trained in control system management. This gap can lead to inefficiencies. Understanding the human factors is as important as system design. Small, unnoticed errors can escalate, causing significant disruption.
Data analysis plays a key role in improvement. Real-time monitoring allows instant adjustments, but it's not always foolproof. Some organizations fail to analyze their data effectively, resulting in missed opportunities. For instance, over-reliance on automation can lead to complacency. Each team member should be encouraged to question and optimize the system wherever possible. Balancing automation with human insight is essential for real success.